publications
“Extraction and characterization of cellulose and cellulose nanocrystals from the stalks of Marrubium vulgareplan”
Muhammad Naveed Khan, Aftab Ahmad, Noor Rehman, Seda KelestemuR, Muhammad Tariq, Abdul Khaliq Jan, Shujaat AhmaD, Dorthe M. Eisele, Wajid Syed, Mahmood Basil A Al-Rawi, Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications, 11, 100947,2025.
Front Cover Article of Issue 27, 2025, Polymer Chemistry.
Nikunjkumar R Visaveliya#, Seda Kelestemur#, Firdaus Khatoon, Jin Xu, Kelvin Leo, Karisma McCoy, Lauren St Peter, Christopher Chan, Tatiana Mikhailova, Visar Bexheti, Geri Shentolli, Anushan Alagaratnam, Saad Ahmed, Piyali Maity, Dorthe M. Eisele*, POLYMER CHEMISTRY, 16, 3111, 2025.
DOI: 10.1039/D5PY00334B
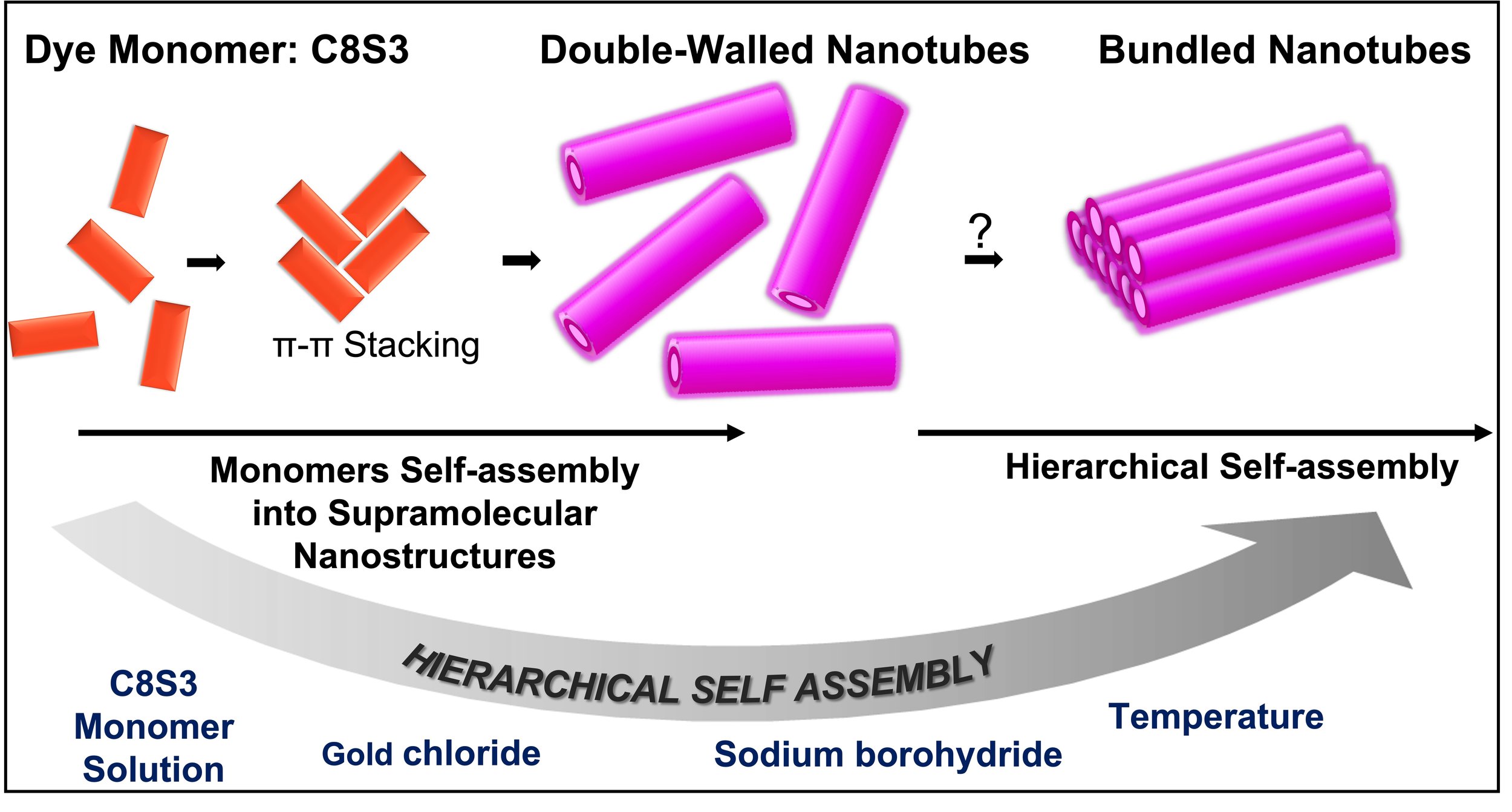
Hierarchical Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Frenkel Excitonic Nanotubes.
SEDA KELESTEMUR, PIYALI MAITY, Nikunjkumar R. Visaveliya, DAMIEN HALPERN, SADIYAH PARVEEN, Firdaus Khatoon, ALI KHALIL, , MATTHEW GREENBERG, QINNGRIU JIANG, , Kara Ng, and Dorthe M. Eisele*, THE JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY B, 2024, 128, 329-339.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c05681
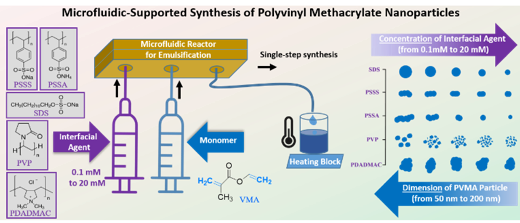
“Microfluidic-supported synthesis of anisotropic polyvinyl methacrylate nanoparticles via interfacial agents”
Nikunjkumar R. Visaveliya, Seda Kelestemur, Firdaus Khatoon, Jin Xu, Kelvin Leo, Lauren St. Peter, Christopher Chan, Tatiana Mikhailova, Visar Bedzeti, Ashni Kapadia, Piyali Maity, William P. Carbery, Kara Ng, and Dorthe M. Eisele*, polymer chemistry, 2022, 13, 4625.
DOI:10.1039/D1PY01729B
Showcasing work from D. M. Eisele and coworkers, The City College of New York at The City University of New York, USA. Microfluidic-supported synthesis of anisotropic polyvinyl methacrylate nanoparticles via interfacial agents By combining the advantages of microfluidics and bulk batch synthesis, D. M. Eisele and coworkers developed a single-step, microfluidic supported synthesis for anisotropic polyvinyl methacrylate (PVMA) polymer nanoparticles with dimensions ranging from 50 nm–200 nm. The cover highlights a SEM image of flower-shaped polyvinyl methacrylate (PVMA) nanoparticles. The research was performed at the NSF Center of Research Excellence in Science and Technology (CREST) for Interface Design and Engineered Assembly of Low Dimensional Systems (IDEALS) at The City College of New York at The City University of New York, USA.
“FRENKEL EXCITONS IN HEAT-STRESSED SUPRAMOLECULAR NANOCOMPOSITES ENABLED BY TUNABLE CAGE-LIKE SCAFFOLDING”
kara NG, Megan WEBSTER, William P. CARBERY, nikunjkumar VISAVELIYA, pooja GAIKWAD, seogjoo j. JANG, ilona KRETZSCHMAR, AND dorthe m. EISELE*, NATURE CHEMISTRY, 2020, 12, 1157-1164.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-020-00563-4
Proof-of-concept demonstration that shows how to overcome barriers to functionalize artificial supramolecular assemblies
Cover article of Volume 4, Issue 22 of Advanced Materials Interfaces
“Surface Wrinkling and Porosity of Polymer Particles toward Biological and Biomedical Applications” (Cover Article)
nikunjkumar r. Visaveliya, Christopher W. Leishman, Kara Ng, Nicolas Yehya, Nelson Tobar, Dorthe M. Eisele*, and Johann Michael Köhler*, Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4, 24, 1770125. doi:10.1002/admi.201770125.
“Room-Temperature Micron-Scale Exciton Migration in a Stabilized Emmisive Molecular Aggregate”
Justin R. Caram, Sandra Doria, Dörthe M. Eisele, Francesca S. Freyria, Timothy S. Sinclair, Patrick Rebentrost, Seth Lloyd, and Moungi G. Bawendi, Nano Letters, 2016 16, 6808-6815. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02529
We report 1.6 ± 1 μm exciton transport in self-assembled supramolecular light-harvesting nanotubes (LHNs) assembled from amphiphillic cyanine dyes.
Quantum Effects in Biology
“Quantum Effects in Biology”
Edited by Mohesi, M., Omar, Y., Engel, G., Plenio, M.B.
“Structured Chromophoric Aggregates” in Chapter 16: Bio-inspired quantum materials”
Sarovar, M., Eisele, D.M., Mohseni, M., Whaley, B.
University Press, Cambridge, 2014.
“Robust Excitons Inhabit Soft Supramolecular nanotubes”
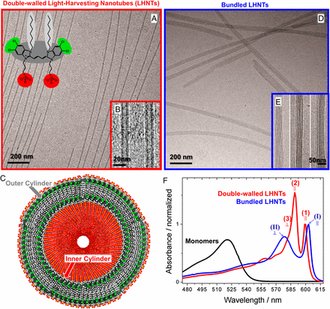
Dörthe M. Eisele, Dylan H. Arias, Xiaofeng Fu, Erik A. Bloemsma, Colby P. Steiner, Russell A. Jensen, Patrick Rebentrost, Holger Eisele, Andrei Tokmakoff, Seth Lloyd, Keith A. Nelson, Daniela Nicastro, Jasper Knoester, and Moungi G. Bawendi, PNAS, 2014, 111 (33) E3367-E3375. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1408342111
Cryo-EM micrograph of double-walled LHNTs self-assembled from amphiphilic cyanine dye molecules
The excitonic system under consideration: Lightharvesting nanotube consisting of a double-walled cylindrical aggregate of amphiphilic cyanine dye molecules.
“Coherent exciton dynamics in supramolecular light-harvesting nanotubes revealed by ultrafast quantum process tomography”
Joel Yuen-Zhou, Dylan H. Arias, Dorthe M. Eisele, Colby P. Steiner, Jacob J. Krich, Moungi G. Bawendi, Keith A. Nelson, and Alán Aspuru-Guzik, ACS Nano, 2014 8, 5527-5534. DOI: 10.1021/nn406107q
“Utilizing Redox-Chemistry to Elucidate the Nature of Exciton Transitions in Supramolecular Dye Nanotubes”
Dorthe M. Eisele, C. W. Cone, E. A. Bloemsma, S. M. Vlaming, C. G. F. van der Kwaak, R. J. Silbey, M. G. Bawendi, J. Knoester, J. P. Rabe, and D. A. Vanden Bout, Nature chemistry, 2012, 4, 598-600. doi:10.1038/nchem.1380
=> Article highlighted in nature chemistry’s ‘news and views’ by Jürgen Köhler “Supramolecular dye aggregates: Nanotube knockout”, Nature chemistry 4, 598-600 (2012)
Light-harvesting nanotube consisting of double-walled cylindrical aggregates of amphiphilic cyanine dye molecules.
The redox chemistry of supramolecular nanotubes self-assembled from amphiphilic cyanine dye 3,3′-bis(2-sulfopropyl)-5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′-dioctylbenzimidacarbocyanine (C8S3) in aqueous solution was investigated by spectroelectrochemistry.
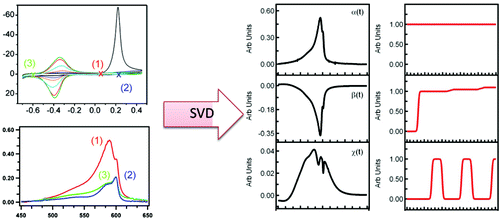
“Singular Value Decomposition Analysis of Spectroelectrochemical Redox Chemistry in Supramolecular Dye Nanotubes”
Craig W. Cone, Sangik Cho, Jennifer L. Lyon, Dörthe M. Eisele, Jürgen P. Rabe, Keith J. Stevenson, Peter J. Rossky, and David A. Vanden Bout ; The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011 115, 14978-14987. DOI: 10.1021/jp2019457
“Photoinduced growth of sub-7 nm silver nanowires within a chemically active organic nanotibular template”
Dörthe M. Eisele, Hans v. Berlepsch, Christoph Böttcher, Keith J. Stevenson, David A. Vanden Bout, Stefan Kirstein, and Jürgen P. Rabe ; Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132, 2104-2105. DOI: 10.1021/ja907373h
Self-assembled supramolecular nanotubes of J-aggregated amphiphilic cyanine dye in aqueous solution are employed as chemically active templates for the photoinitiated formation of silver nanowires with a very small and homogeneous diameter of (6.4 ± 0.5) nm.
Graphene‐based optically transparent electrodes (G‐OTEs; see image) with high conductivity, optical transparency, and chemical stability are fabricated by deposition of exfoliated graphite oxide onto quartz substrates, followed by thermal reduction.
“Graphene-based optically transparent electrodes for spectroelectrochemistry in the UV-Vis Region”
Constans M. Weber, Dörthe M. Eisele, Jürgen P. Rabe, Yanyu Liang, Xinliang Feng, Linjie Zhi, Klaus Müllen, Jennifer L. Lyon, Ryan Williams, David A. Vanden Bout, Keith J. Stevenson, Small, 2010, 6, 184-189. doi:10.1002/smll.200901448
“UV-vis Spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry investigations of tubular J-aggregates of amphphilic cyanine dyes”
Jennifer L. Lyon, dorthe Eisele, stefan Kirstein, Jürgen Rabe, david Vanden Bout, and keith J. Stevenson, ECS Transactions, 2009. 16. DOI:10.1149/1.3104058
Cylindrical chiral double-walled nanotubular J-aggregates of an amphiphilic cyanine dye molecule
“Uniform exciton fluorescence from individual molecular nanotubes immobilized on solid Substrates” (Cover Article)
Dörthe M. Eisele, Jasper Knoester, Stefan Kirstein, Jürgen P. Rabe & David A. Vanden Bout. Nature Nanotechnology, 2009, 4, 658–663. doi:10.1038/nchem.1380.
“Spectroelectrochemical Investigation of Double-Walled Tubular J-Aggregates of Amphiphilic Cyanine Dyes”
Jennifer L. Lyon,†, Dörthe M. Eisele,‡, Stefan Kirstein,‡, Jürgen P. Rabe,‡, David A. Vanden Bout,† and, and Keith J. Stevenson*,† ; The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112, 1260-1268. DOI: 10.1021/jp077412f
SCHEME 1: (Left to Right) Chemical Structure of C8S3 Cyanine Dye, Showing the Most Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Regions; Simple Sketch of Bilayer Formation (Not Scaled); Top View of Double-Walled Tubule Formed by the Bilayer (Not Scaled, Simplified); Three-Dimensional Image of Helical, Double-Walled Tubule